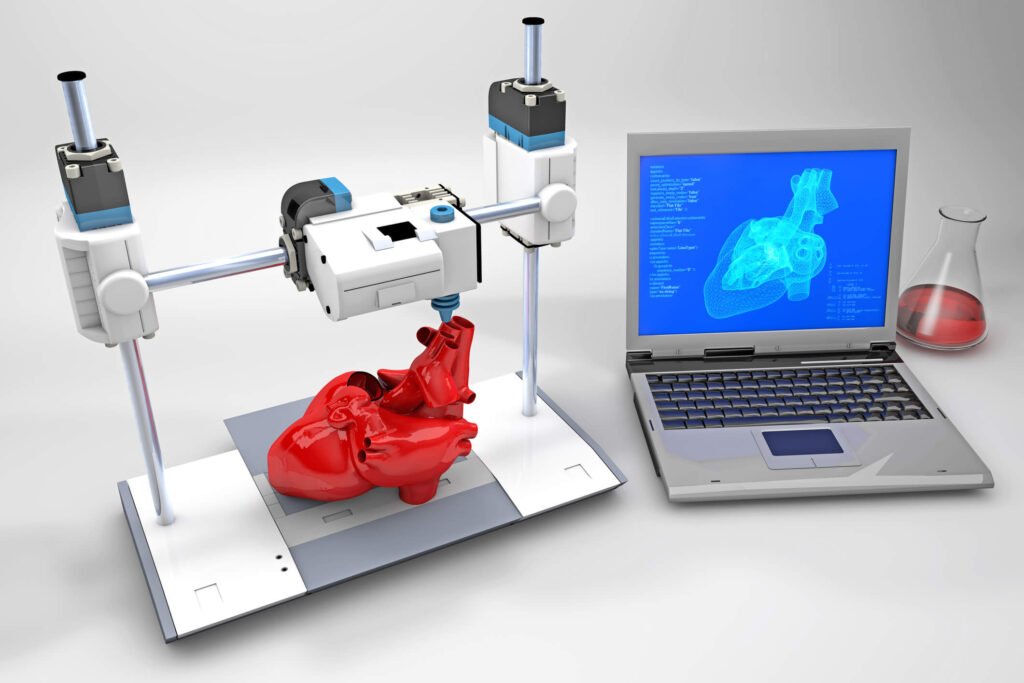
In the ever-evolving healthcare industry, 3D printing is a technological phenomenon reshaping medicine. What started as an unimaginable concept has become a cornerstone of medical innovation, offering many unique applications that have redefined patient care, medical research, and surgical techniques. As technology continues to change, some for the better and others for the worse, 3D printing has impacted society today.
The specialty of prosthetics has seen a shift with the creation of 3D printing, permitting custom and functioning limbs. This technology has brought hope and mobility to numerous patients and improved people’s lives. Furthermore, the innovation of patient-specific implants has transformed surgical procedures. Surgeons now access implants designed for a patient’s unique anatomy, creating better outcomes and decreasing recovery times. From orthopedic implants to dental prosthetics, 3D printing has boosted patient care by leaps and bounds.
Beyond physical implants, 3D printing has embarked on complex organ and tissue printing. While the concept of printing human organs continues to be researched and tested, there have been advancements in what is now known as ‘bioprinting.’ Researchers are investigating possibilities of producing active tissues and organs using bioinks composed of living and active cells. Although it needs examination, this innovation bears immense hope for the future of personalized medicine.
However, 3D printing has been used for more than direct patient care. Medical education and training have gone through a transformation through the utilization of 3D printing. Intricate models are now being printed with exceptional accuracy, allowing medical students and professionals with tangible, hands-on learning tools. This immersive approach improves understanding and skill, equipping healthcare providers with complex procedures with elevated precision.
Continuous innovation in materials and advances in printing techniques can unlock new boundaries in medicine. 3D printing foreshadows a future where personalized healthcare resolutions are not just a possibility but an everyday reality. Nevertheless, challenges persist, ranging from regulatory hurdles to the ethical considerations of printing human tissues and organs. As these technologies evolve, a delicate balance must be struck between innovation and ethical responsibility to ensure safe, equitable, and accessible healthcare solutions for all.
In conclusion, the trajectory of 3D printing in medicine is nothing short of remarkable. From enhancing patient care to transforming surgical procedures and pushing the boundaries of regenerative medicine, its impact is profound and far-reaching. As we navigate this era of unprecedented innovation, the fusion of 3D printing and healthcare promises a future where healing and innovation intertwine to redefine the possibilities of medicine.
Works Cited
“What Is 3D Printing? How Does a 3D Printer Work? Learn 3D Printing.” 3D Printing, 21 Nov. 2023, 3dprinting.com/what-is-3d-printing/. Accessed 01 Jan. 2024.
How Do Hurricanes Affect Your Drinking Water?
“What Is Medical 3D Printing and How Does It Work?” Synopsys, www.synopsys.com/glossary/what-is-medical-3d-printing.html#:~:text=Medical%203D%20printing%20is%20increasingly,known%20as%20additive%20manufacturing)%20processes. Accessed 01 Jan. 2024.
“Introduction to Medical 3D Printing and 3D Printers for Healthcare.” Formlabs, formlabs.com/blog/3d-printing-in-medicine-healthcare/. Accessed 01 Jan. 2024.